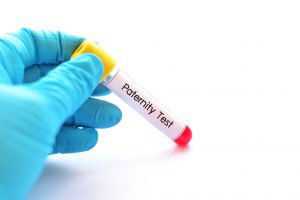
 A person may rescind a Texas acknowledgement of paternity no later than 60 days after its effective date, or earlier if a court proceeding on an issue relating to the child is initiated. Once this time passes, the party may challenge the acknowledgement only on the basis of fraud, duress, or material mistake of fact. Tex. Fam. Code § 160.307. Under current law, a proceeding challenging the acknowledgment may be commenced any time before an order affecting the child is issued. Tex. Fam. Code § 160.308. That statute was amended in 2011, however. Suits challenging acknowledgements signed before September 1, 2011 must be filed within four years of the date the acknowledgement was filed with the state.
A person may rescind a Texas acknowledgement of paternity no later than 60 days after its effective date, or earlier if a court proceeding on an issue relating to the child is initiated. Once this time passes, the party may challenge the acknowledgement only on the basis of fraud, duress, or material mistake of fact. Tex. Fam. Code § 160.307. Under current law, a proceeding challenging the acknowledgment may be commenced any time before an order affecting the child is issued. Tex. Fam. Code § 160.308. That statute was amended in 2011, however. Suits challenging acknowledgements signed before September 1, 2011 must be filed within four years of the date the acknowledgement was filed with the state.
In a recent case, a man, identified in the appeals court’s opinion by the pseudonym “William,” attempted to challenge an Acknowledgement of Paternity he had signed and filed in 2005. William petitioned the trial court to set aside the acknowledgment in September 2019 “on the basis of fraud, duress, or material mistake of fact.” He did not, however, make specific allegations. The mother argued the petition was time-barred.
Only William testified at the trial. The mother did not appear or participate. The trial court found the petition was untimely and denied it.
 Texas Divorce Attorney Blog
Texas Divorce Attorney Blog

 Grandparents sometime take on a parental role in the lives of their grandchildren. In some circumstances, such grandparents may have standing (i.e., the right to sue) for possession and access to the children. Parents have a fundamental right to make decisions regarding their children, however. Generally, a court in a Texas custody case cannot interfere with a fit parent’s right to make decisions for their child by awarding access or possession to a non-parent over the fit parent’s objection, unless the nonparent overcomes the presumption that the fit parent is acting in the child’s best interest. In a recent case, a father
Grandparents sometime take on a parental role in the lives of their grandchildren. In some circumstances, such grandparents may have standing (i.e., the right to sue) for possession and access to the children. Parents have a fundamental right to make decisions regarding their children, however. Generally, a court in a Texas custody case cannot interfere with a fit parent’s right to make decisions for their child by awarding access or possession to a non-parent over the fit parent’s objection, unless the nonparent overcomes the presumption that the fit parent is acting in the child’s best interest. In a recent case, a father  A court should consider a number of factors in deciding a Texas custody case. Even when the court determines the parents should be joint managing conservators, the court does not have to award equal periods of possession and access to the child to each parent. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.135. Under Texas law, there is a rebuttable presumption that the standard possession order serves the child’s best interests. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.252. A father recently
A court should consider a number of factors in deciding a Texas custody case. Even when the court determines the parents should be joint managing conservators, the court does not have to award equal periods of possession and access to the child to each parent. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.135. Under Texas law, there is a rebuttable presumption that the standard possession order serves the child’s best interests. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.252. A father recently  A parent’s behavior may affect their rights to access and possession of their child in a Texas custody case. In a recent case, the trial court’s order provided that the schedule would change if the child had a certain number of unexcused absences or instances of tardiness while in the mother’s care.
A parent’s behavior may affect their rights to access and possession of their child in a Texas custody case. In a recent case, the trial court’s order provided that the schedule would change if the child had a certain number of unexcused absences or instances of tardiness while in the mother’s care. When a court considers Texas child custody and visitation, the child’s best interest is the primary concern. The court considers certain factors, including what the child wants, the child’s current and future needs, any danger to the child, the parents’ respective abilities, programs available, the parents’ plans for the child, stability, any acts or omissions indicating the relationship between the parent and child is not proper, and any excuse for those acts or omissions.
When a court considers Texas child custody and visitation, the child’s best interest is the primary concern. The court considers certain factors, including what the child wants, the child’s current and future needs, any danger to the child, the parents’ respective abilities, programs available, the parents’ plans for the child, stability, any acts or omissions indicating the relationship between the parent and child is not proper, and any excuse for those acts or omissions.

 Texas family law has a strong presumption that it is in the child’s best interest to give custody to a parent. Generally, the court must appoint sole managing conservatorship to the parent instead of a non-parent unless it finds doing so would not be in the child’s best interest due to significant impairment of the child’s emotional development or physical health. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.131(a). What if the parent lives in another country? A Texas appeals court
Texas family law has a strong presumption that it is in the child’s best interest to give custody to a parent. Generally, the court must appoint sole managing conservatorship to the parent instead of a non-parent unless it finds doing so would not be in the child’s best interest due to significant impairment of the child’s emotional development or physical health. Tex. Fam. Code § 153.131(a). What if the parent lives in another country? A Texas appeals court